Half-cut solar cells are, as the name implies, typical silicon solar cells that have been sliced in half by a laser cutter. REC Solar pioneered half-cut solar photovoltaic cells in 2014 with the goal of increasing the energy production of solar panels.
Half-cut cells provide a number of advantages over standard solar cells. In terms of performance, half-cut cells can boost panel efficiencies by a few percentage points. They outperform standard cells and are more physically robust than their typical counterparts. They are more resistant to breaking due to their smaller size
How do half-cut solar cells work?
Half-cut solar cell technology increases the energy output of solar panels by reducing the size of the cells, so more can fit on the panel. The panel is then split in half so the top operates independently of the bottom, which means more energy is created – even if one half is shaded.
Let’s look at it in more detail –
The cells are cut in half with a laser. By cutting these cells in half and Solar cells are reduced in size –
- Traditional solar panels usually have 60 to 72 solar cells, and half-cut panels have 2X i.e. 120 to 144 cells.
- The current within the cells is halved, which reduces the resistive losses from traveling energy, which, in turn, equals better performance.
- The panel itself is then split in half so that the top and bottom portions operate as two separate panels – generating energy even if one part is shaded.
The key to half-cut cell design is a different method of “series wiring” for the panel, or the way the solar cells are wired together and pass electricity through a bypass diode within a panel. The bypass diode, indicated by the red line in the images below, carries the electricity that the cells generate to the junction box.
In a traditional panel, when one cell is shaded or faulty and does not process energy, the entire row that is within the series wiring will stop producing power.
For example, let’s take a look at the traditional 3-string series wiring method:
With the traditional full cell string series wiring, shown above, if a solar cell in Row 1 does not have ample sunlight, every cell within that series will not produce energy. This knocks out a third of the panel.
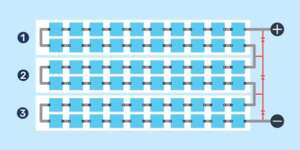
A half-cut, 6-string solar panel works a bit differently:
If a solar cell in Row 1 is shaded, the cells within that row (and that row only) will stop producing power. Row 4 will continue to produce power, generating more energy than a traditional series wiring because only one-sixth of the panel has stopped producing power, instead of one-third.

You can also see that the panel itself is split in half, so there are 6 total cell groups instead of 3. The bypass diode connects in the middle of the panel, instead of on one side like the traditional wiring above.
Advantages Of Half-cut Solar Cells?
- They boost power production and performance of solar modules with their unique wiring arrangement, which allows them to tolerate more shadow
- They offer a greater wattage than standard panels, resulting in more electricity per square foot.
- Lower hot spots: Hot spots are caused by the movement of surplus heat on a panel – from an extremely hot portion to a shaded, cooler section. Hot spots are less destructive in a half-cut cell since there are more cells to distribute the surplus heat to.
- Reduced resistive losses: Resistive losses, or power lost during electrical current transit, are one form of power loss when solar cells convert sunlight into electricity. When solar cells are chopped in half, less current is generated from each cell, resulting in lower resistive losses.
Most of the solar panels now used are Monocrystalline PERC Half Cut panels. Half-cut cells helps to maximize the efficiency of the sunlight, optimizes the surface area being used for solar and maximizes net metering benefits. Unless you have an reason otherwise, insist with you installer to go for half-cut technology.







